
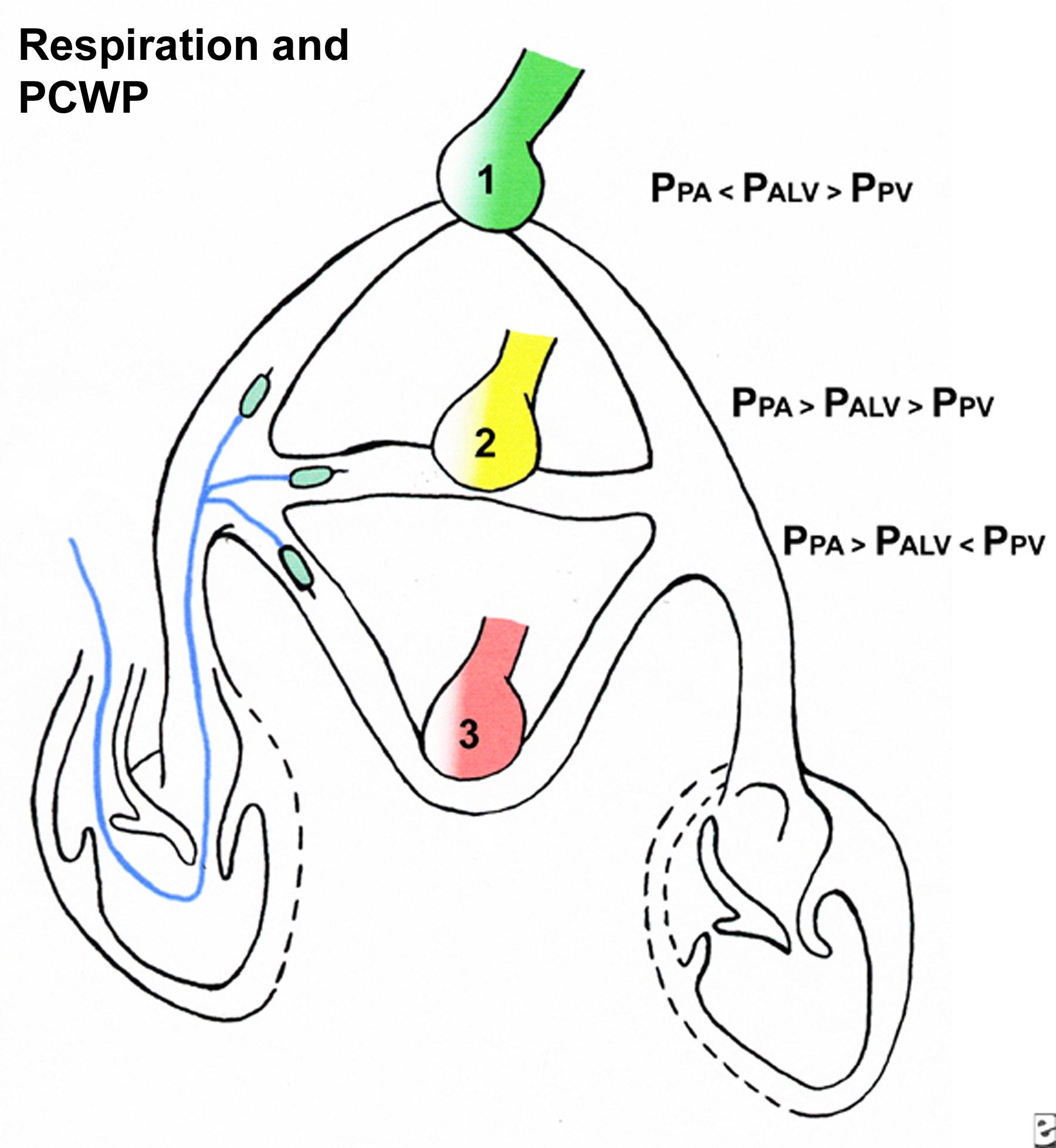
LVEDV and PWP, the PWP accounted for less than 5% of the explained variance in the stroke volume index. Clinically, the PCWP is the pressure measured by wedging a pulmonary catheter with an inflated balloon into a small pulmonary arterial branch. Of the left ventricular ejection fraction. Patients in this PH subgroup may have pulmonary artery pressures (PAP) in proportion to their elevated PCWP (pulmonary venous hypertension, PVH) or higher. Within each group, no relationship was found between the LVEDV and the PWP however, when omitting the effect of PEEP, a modest correlation was noted ( r = 0.302 p < 0.01). Mean PCWP and LAP were linearly related (LAP 0.66PCWP + 4.5 cm H2O,, and ) over a wide range of high and low CPAP values during APRV. The authors assessed the relationship between left ventricular preload measured as the left ventricular end-diastolic volume (LVEDV), and the PWP, in acutely ill patients with sepsis and cardiac disease. Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure Pulmonary artery catheterization: Interpretation of hemodynamic values and waveforms in adults Cardiac catheterization. The pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PWP) is the index of left ventricular filling pressure most frequently utilized as representative of left ventricular preload. The pulmonary wedge pressure (PWP), also called pulmonary arterial wedge pressure (PAWP), pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP), pulmonary artery occlusion. The construction of a Frank-Starling myocardial function curve relating heart work to left ventricular preload is clinically utilized to assess therapeutic protocols in critically ill patients.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
